
Development and Implementation of Ayurvedic and Unani Practices in the Delhi Sultanate

Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia in Ancient Africa
Alzheimer’s Disease is extremely prevalent in African Americans compared to Caucasians, ranging from around 14% to almost 100% higher. Additionally, African Americans have a much higher chance of developing AD. There is a greater familial risk, and they are 1.5 times as likely to develop the disease compared to non-African Americans. However, as seen from many different sources, AD presents itself differently depending on the race, gender, or age of the patient, and in African Americans, genetic and environmental factors have a more significant impact on the patient.
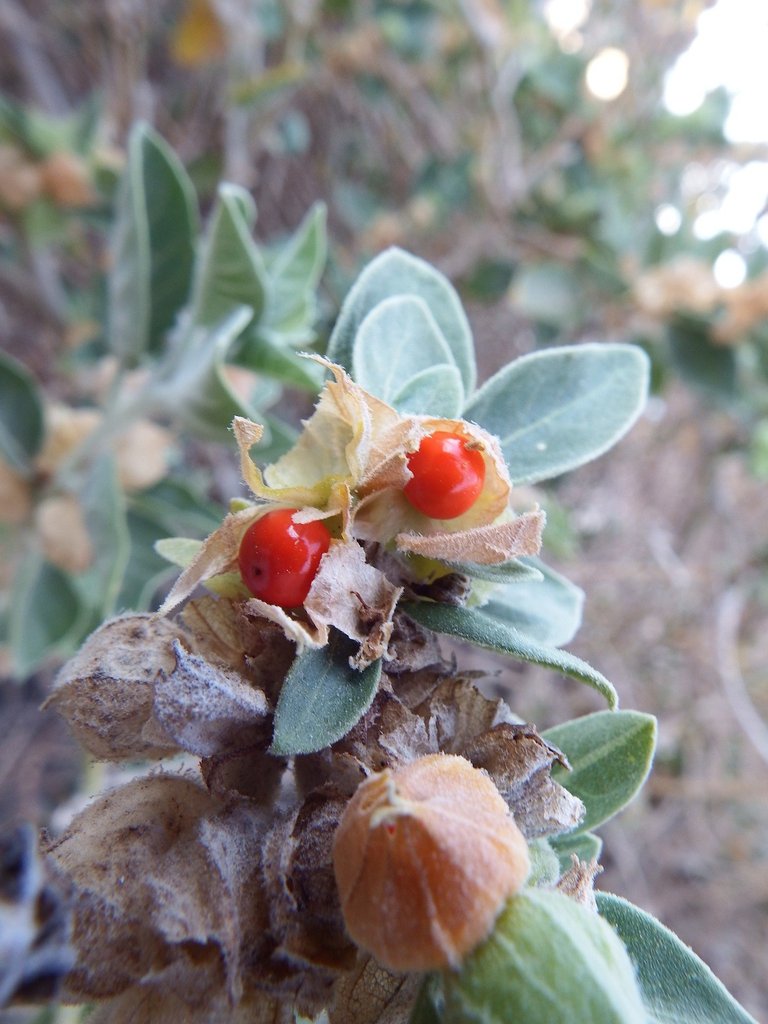

Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia in Ancient India
Similar to ancient China, ancient Indian treatment of AD dementia involved herbs and multi-target approaches including non-pharmacological methods like mantra therapy, psychotherapy, yoga, and meditation, as opposed to pharmacological approaches of Western culture. The history of Indian medicine dates back to the Vedic Age (around 1500 BC), followed by the traditional Indian system of Medicine, Ayurveda, around the middle of the 1st millennium BC. Ayurvedic medicine is based on a more holistic view of treatment, including over 700 herbs and 6,000 formulations to treat diseases. Herbs, like Mucuna Pruriens (Velvet Bean), Withania Somnifera (Ashwaganda), Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), Centella Asiatica (Gotu Kola), and Curcumin (Turmeric) were used to specifically treat neurodegenerative diseases and have recently been proven to be effective.
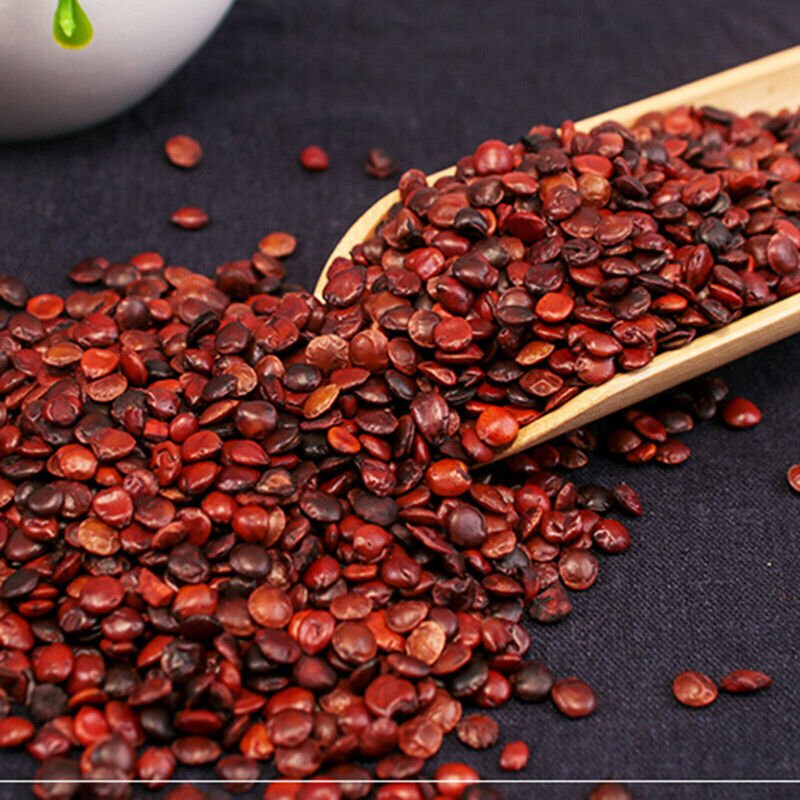

Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia in Ancient China
Instead of medications and therapies, treatment of dementia in ancient China consisted of the use of a multitude of herbs thought to improve mental function. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), has been used to treat neurogenerative diseases in China and other Asian countries, it uses a holistic multi-target treatment approach. a popular method to treat these cognitive diseases. One treatment for improving cognition in ancient China was Suan Zao Ren Decoction (SZRD) which has five herbal Chinese medicines, including Suanzaoren and other Chinese roots. It was documented in the classical Chinese medical book JinGuiYaoLue (Synopsis of Prescriptions of the Golden Chamber) by Zhang Zhongjing (AD 152-219) and has been found to improve cognitive impairment and repair neuron damage6. Another herbal combination described in Wang Tao’s Treatise (752 A.D.) is called Huanglian Jiedu Decoction included the following components components- Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri, and Fructus Gardeniae.
Treating an Alzheimer’s Patient
As I mentioned two blog posts ago, I’m going to discuss the treatments from various ancient cultures and see how they can be applied to how Alzheimer’s is treated now. But, before I do that, in this blog post, I want to outline the different drugs and care approaches that are being employed right now for Alzheimer’s patients in the United States.